Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructureand Thermo Physical Properties of Plasma SprayedZrO2–7%Y2O3 and La2Zr2O7 Coatings
Peer-reviewed Papers
Authors:
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Kirsten Bobzin,
Dr.-Ing. Mehmet Öte,
Dipl.-Ing. Thomas Frederik Linke,
Dr.-Ing. Lidong Zhao,
M.Sci. Garip Erdogan,
Prof. Dr. Fatih Üstel
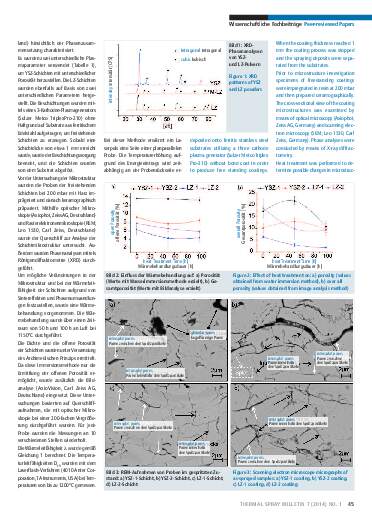
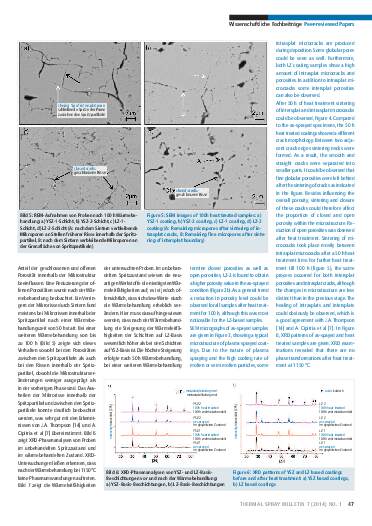
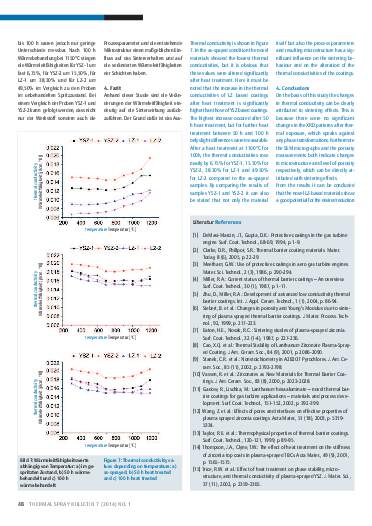
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) are inseparably linked to jet engines. The microstructure of these coatings significantly affects their physical properties. As a mutual feature of the microstructure of plasma sprayed coatings, porosity is a significant factor, because its development depends strongly on process characteristics. Therefore, there is a need to establish quantitative relationships between the microstructure and physical properties in order to design an ideal coating microstructure. Limitations of using conventional TBCs have also led the research direction towards the development of new promising top coat materials. To evaluate microstructural transformation of the coatings as a consequence of heat treatment as well as to investigate thermophysical properties of TBCs consisting of ZrO2–7%Y2O3-based (mass fraction) and La2Zr2O7-based materials, freestanding coatings were produced with different levels of porosities, within this study. After 50 hours and 100 hours of heat treatment at 1150°C the coatings were characterized to investigate their morphology, phase composition, porosity and thermal conductivity.
Order this article as a PDF for 8.00 Euro. Send us a short e-mail with your details.