Influence of Boron Content on Microstructure andProperties of Wire-arc Sprayed Fe-based Coatings
Peer-reviewed Papers
Authors:
M. Sc. Haihua Yao,
Dr. Zheng Zhou,
Dr.-Ing. Yiming Wang,
Prof. Dr. Ding-Yong He,
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Kirsten Bobzin,
Dr.-Ing. Lidong Zhao,
Dipl.-Ing. Thomas Frederik Linke,
Dipl.-Ing. Tim Königstein
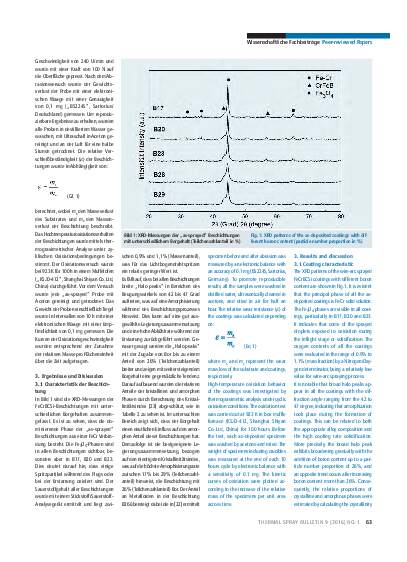
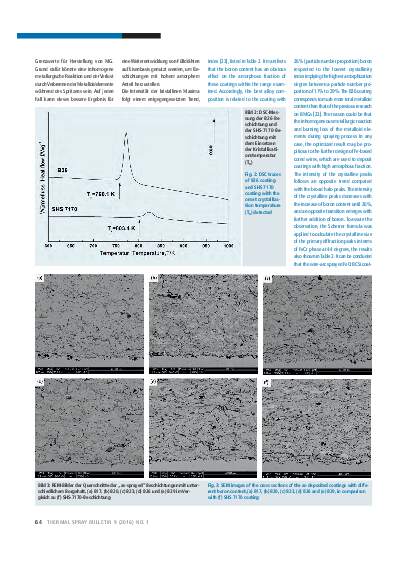
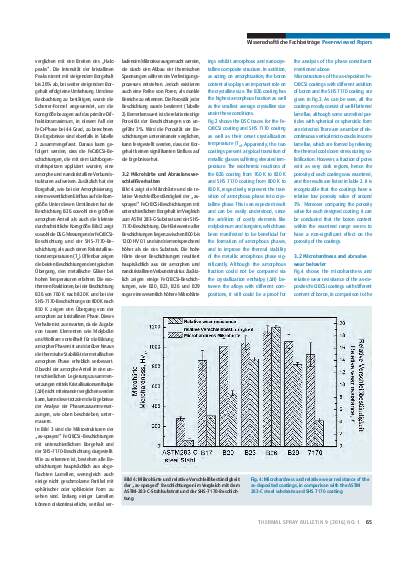
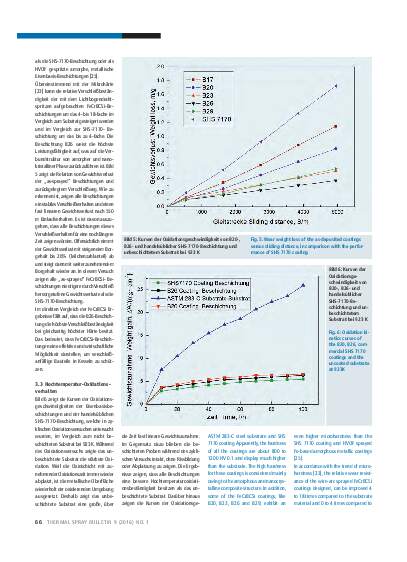
A series of FeCrBCSi coatings were prepared by wire-arc spraying to investigate the influence of the boron content on the microstructure and properties of the coatings. Microstructural studies show that the as-deposited coatings present a dense layered structure with porosity around 3%, and a microstructure primarily composed of amorphous and nanocrystalline phases. It is found that the increase of boron content within the composition range examined exhibits a significant effect on the phase composition, as well as the microhardness and wear resistance of the coatings. The composite phase structure at a boron content of 26% (particle number proportion), leads to the best performance of the coating observed within this study, in terms of higher amorphous fraction and reduced nanocrystalline size distribution. The relative wear resistance of this coating is about 18 times higher than that of ASTM 283-C steel and 4 times higher than commercially available SHS 7170 coating. After cyclic oxidation at 923 K, the weight gain of the novel FeCrBCSi coating is significantly lower than the uncoated substrate, and approaches the performance of a SHS 7170 coating.
Order this article as a PDF for 8.00 Euro. Send us a short e-mail with your details.