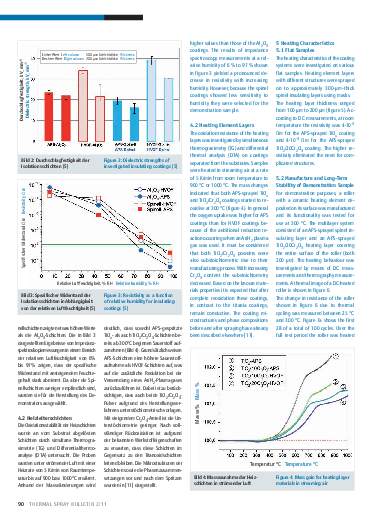
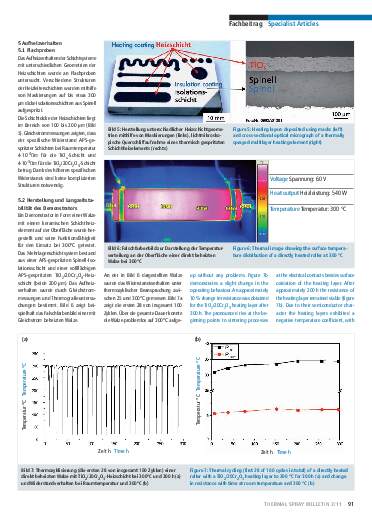
Thermally sprayed multilayer ceramic heating elements
Specialist Article
Authors:
Dipl.-Ing. (FH) Stefan Scheitz,
Dr. Filofteia-Laura Toma,
Dr.-Ing. Lutz-Michael Berger,
Dipl.-Ing. Roberto Puschmann,
Dr. Viktar Sauchuk,
Dr.-Ing. Mihails Kusnezoff
Thermally sprayed multilayer heating elements composed of ceramic electrically insulating and conductive layers can be used effectively for the tempering and heating of machine and system components. In humid environments spinel (MgAl2O4) layers are preferable to electrically insulating APS- and HVOF-sprayed Al2O3 layers. Depending on the operating temperature, heating layers made from titanium suboxides (TiOx) or from compositions in the Cr2O3-TiO2 system can be used. These ceramic layers offer a number of advantages over metal heating layers, including a lower thermal expansion coefficient mismatch between
layers. Reoxidation to titanium dioxide limits the upper operating temperature of titanium suboxide heating layers in air to approximately 250°C. Heating layers made from materials in the Cr2O3-TiO2 system have higher maximum operating temperatures. A coated roller is used to demonstrate the functioning of the ceramic multilayer heating elements at an operating temperature of 300°C.
Order this article as a PDF for 8.00 Euro. Send us a short e-mail with your details.